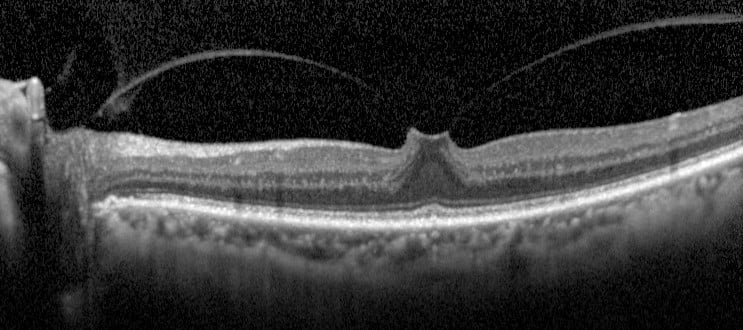
Vitreomacular traction (VMT) occurs when the vitreous separates from the retina, except at the macula. Residual vitreomacular adhesion pulls on the macula, distorting tissue. Best seen with optical coherence tomography (OCT).
OCT image showing VMT.
Normal OCT.
Symptoms
Foveal distortion causes corresponding visual distortion (metamorphopsia) and blurred vision. Symptoms may be worse than predicted based on visual acuity.
Treatment
Mild, asymptomatic VMT may be observed. Symptomatic cases, or those evolving to a macular hole, may require treatment with an intravitreal injection of ocriplasmin, so-called chemical vitrectomy, or more commonly pars plana vitrectomy, to remove the vitreous and release traction.
Referral guidance
Refer routinely. Further information is available in the patient information leaflet.