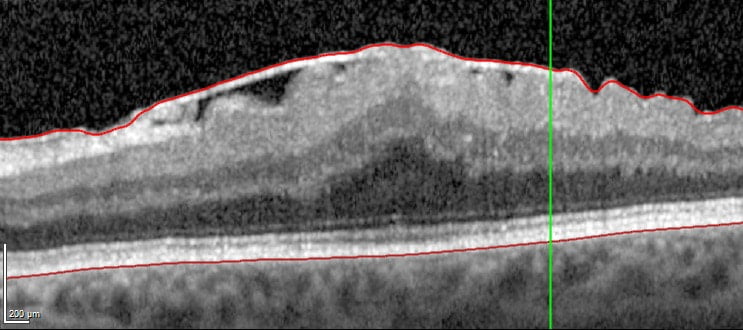
An epiretinal membrane (ERM) occurs when a very thin layer of scar tissue forms on the surface of the macula. The macula is the light sensing layer inside the very back of the eye. The epiretinal membrane may contract, distorting the macula.
OCT scan showing an ERM on top of the retina, with thickening of the macular and distortion of the inner retinal surface.
Normal OCT.
What are the symptoms of an epiretinal membrane?
Epiretinal membranes may be quite stable and not have much effect on vision. However, some epiretinal membranes get progressively worse, causing blurring and/or distortion of vision. People sometimes notice a film or smudge in their vision.
Do I need surgery for epiretinal membrane?
If your epiretinal membrane is severe enough to cause you trouble with your vision and everyday life, you may decide to have eye surgery to remove the membrane. Professor Jackson can help you weigh up the pros and cons of surgery in your case.
Epiretinal membrane surgery speeds up the development of cataract. Hence, some people opt to combine epiretinal membrane surgery with cataract surgery, to avoid two operations.
Further information about epiretinal membranes and the risks and benefits of surgery can be found in the patient information leaflet.